Enterprise Methodologies |
|
|
|

|
| Category | Type 1 (Generic) Methodology and Architecture |
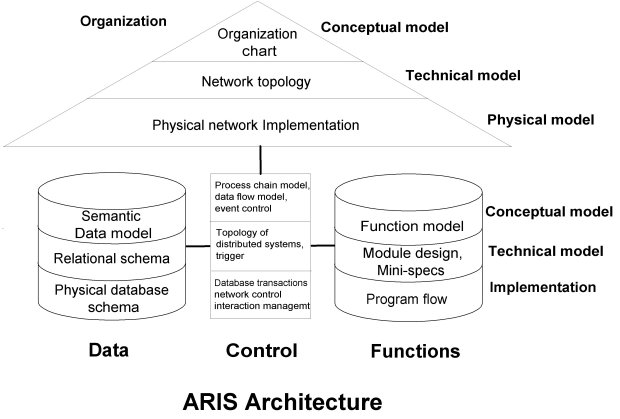
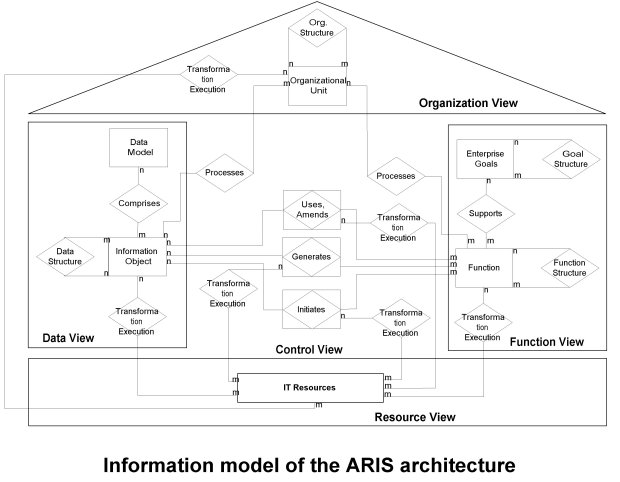
| Summary | The ARIS-architecture distinguishes between
Organization, Function, Information and Control views. It uses a
graphic modelling system supported by software which models data
movement and tasks.
ARIS focuses on the analysis and requirements definition phase during the design of managerial information systems, not on the execution of business processes. |
| Comments | ARIS provides a generic and well-documented
methodological framework. It is closely associated with SAP to which it
can directly export models for incorporation in SAP systems.
Software is complex to use and has relatively long learning curve. |
In ARIS, business processes are described by process chain diagrams. The modeling is done using a tool set instead of a language. Several sub-tools are available, each displayed in its own window. The information captured by the ARIS tool set is stored in a database following the ERM (Entity-Relationship-Model). In Scheer (1994) it is argued that a formal language imposes restrictions on the day-to-day usability by potential end users.
Relationship to PERA
The following describes how this methodology fits within the PERA GERAM.
The yellow background on the PERA diagram indicates where this methodology is most commonly applied. Click on the PERA diagram for more explanation.
| Industry | Widely applicable to large-scale industrial and business enterprises off all types including descrete and process manufacturing, service industries, government and military. |
|
| Enterprise Phases: | Preliminary Engineering: Used to
perform workflow analysis, resulting in functional or procurement
specifications. Modeling predicts "bottlenecks" and time delays.
Detail Engineering: May be used for direct transfer of functional definitions to SAP. May also be used to maintain Construction Phase:May be used during Implementation to guide acceptance testing. Operations Phase:May be used to maintain workflows and model the effect of proposed modifications. |
|
| Enterprise Elements: | Facilities: N/A
People: Relates to Human and Organizational tasks to the extent that these are automated. May be used to detail interfaces with automated information systems. Control & Info Systems: Used in Information Systems but not plant automation. |
The ARIS Model and its application in relationship to PERA, CIMOSA and other Type 2 Models is discussed in the paper "Workflow Management within the ARIS Framework"